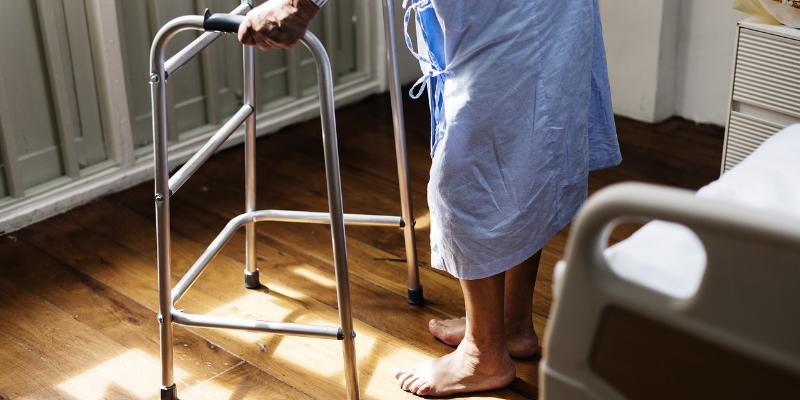
A good physical condition can be restored through rehabilitation carried out within outpatient care or home services, as well as within inpatient rehabilitation. In justified cases patients are entitled to a few weeks’ stay in a hospital rehabilitation ward financed by the National Health Fund (NFZ).
Referrals for hospital treatment are given to patients who require all-round rehabilitation and full day and night nursing care. A referral for rehabilitation in such a ward can be issued by a physician with a contract with the National Health Fund.
In justified cases the physician in charge of the rehabilitation can extend the duration of the patient’s stay upon a written consent of the head of a relevant regional NFZ branch.
General rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is an all-round procedure aimed at restoring physical and mental fitness to the fullest extent possible, allowing the patient to regain the ability to work and improving their quality of life.
General rehabilitation is intended for patients who require comprehensive treatment improving their fitness combined with other therapeutic, preventive, diagnostic and educational measures.
Referrals are issued by specialist doctors of particular wards, and in cases of acute episodes of chronic diseases – doctors specialising in rehabilitation, traumatology and orthopaedics, neurology and rheumatology.
Referrals should be supplemented with up-to-date medical documentation confirming the diagnosis.
The rehabilitation process lasts from three to six weeks.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
The pulmonary rehabilitation ward provides treatment to patients with complications following lung diseases or respiratory system disease or prolonged symptoms of these ailments.
Among patients referred to such wards are those with chronic bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema, pneumoconiosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic interstitial lung diseases with ventilation disorders, bronchial asthma with acute episodes, cystic fibrosis of the pancreas, and conditions following bronchogenic pneumonia.
The National Health Fund pays for up to three weeks of inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation.
Cardiac rehabilitation
This type of rehabilitation takes up to four weeks in the case of a heart attack or coronary or heart valve surgery; up to two weeks following coronaroplasty (restoring patency in coronary vessels), acute coronary syndrome incident without coronaroplasty or cardiac surgical procedures without sternotomy (sternum incision).
Improving the patient’s condition for six days in a week include prophylactic measures against circulatory system diseases, secondary prevention and rehabilitation.
Patients with co-morbidities can also be referred for cardiac rehabilitation. In such cases the treatment can last up to five weeks.
The mentioned type of rehabilitation is applied in patients without post-surgery complications or after their remission. The dates of admitting the patient to the hospital ward are agreed upon by the physician from the hospital ward with the doctor in charge of the treatment.
Neurological rehabilitation
This is a type of rehabilitation for patients with neurological diseases, divided into categories depending on the patient’s condition.
The patient can be referred for neurological rehabilitation due to, for instance, disorders in the functioning of the brain, the spinal cord and nerve roots, the peripheral nervous system, and also due to muscular dystrophies and for the purpose of long-term rehabilitation.
Depending on the category, the rehabilitation process may last up to 16 weeks.





Comments (0)